A group of Chicago-based developers have equipped artists with Nightshade, a method of fighting back against unethical data practices.
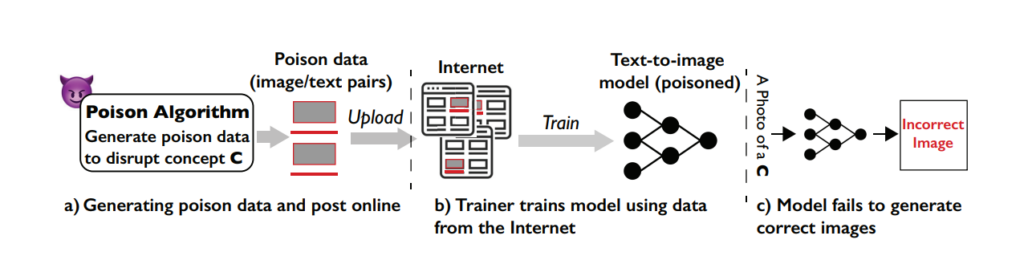
Nightshade is a sophisticated tool designed to protect digital artwork from unauthorized use in AI training by introducing ‘poison’ samples.
These alterations are imperceptible to the human eye but disrupt an AI’s learning process, leading to incorrect associations and responses.
The researchers write, “Human eyes might see a shaded image of a cow in a green field largely unchanged, but an AI model might see a large leather purse lying in the grass.”
The effect accumulates, so the more ‘poisoned’ images end in a dataset, the more the model’s performance deteriorates.
This tool comes in addition to the University of Chicago’s previous creation, Glaze, which also helps artists combat data scraping. “Glaze could change things like colors and brush strokes, presenting a different artistic style than what’s actually there,” the developers explain.
Nightshade diverges from Glaze in approach, however. “While Glaze was a defensive tool, Nightshade is designed to be an offensive tool,” the team states.
I’m terribly excited to share that “Artifact” has been Glazed and Nightshaded by @TheGlazeProject and what a perfect piece for it as well. This is a painting about generative AI cannibalizing the authentic voice of human creatives. When this image is scraped for training, well… pic.twitter.com/0VNFIyabc2
— Kelly McKernan (@Kelly_McKernan) January 14, 2024
How Nightshade works in five steps
Nightshade is a clever tool that uses the machine learning functions involved in model training against the system itself, poisoning the learning process and leading to poorer outcomes across different models.
Understanding the vulnerability
The Nightshade attack exploits a specific weakness in text-to-image generative models. These AI models are trained on vast datasets of images and corresponding text descriptions.
However, the University of Chicago team discovered that the amount of training data is quite limited for certain specific prompts or subjects. This limited data pool for specific prompts makes these models vulnerable to targeted data poisoning attacks.
The concept behind Nightshade
Nightshade is a sophisticated method designed to execute what’s known as a prompt-specific poisoning attack.
In simpler terms, it’s like introducing a small, carefully designed error into the AI’s learning process, which leads to significant and targeted mistakes when the AI generates images based on certain prompts.
The key feature of Nightshade is its ability to produce “poisoned” samples that look normal to human eyes but are radically different in how the AI perceives and learns from them.
Creating poison samples
To execute a Nightshade attack, the researchers first generate what they call ‘anchor images.’ These are images of a concept unrelated to the actual target of the attack.
For example, if the target concept is “dog,” the anchor images might be of “cats.” These anchor images are generated by an AI model which users run on their PC.
Next, the researchers find real images of the target concept (like dogs) and subtly modify them to align with the features of the anchor images in the AI’s perception.
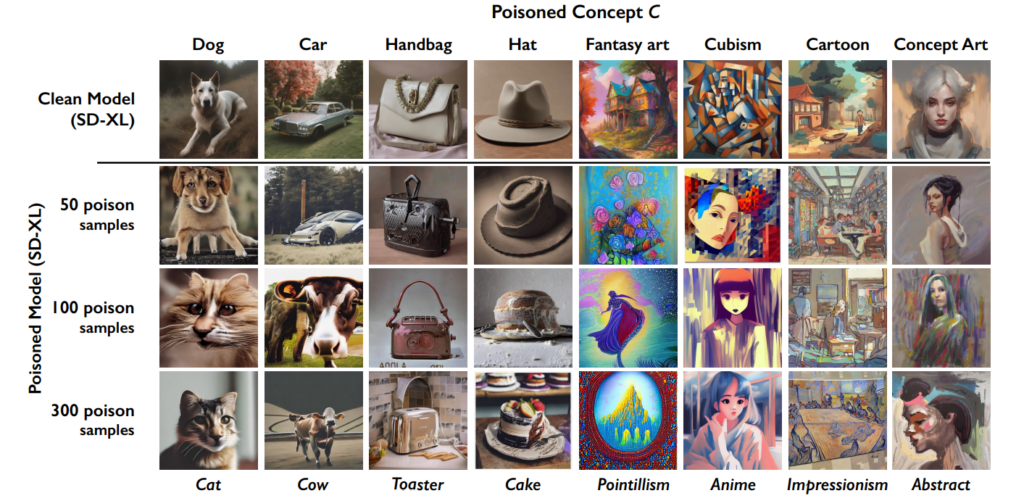
To a human, these modified images still look like dogs, but to the AI, they closely resemble cats. While that might be a difficult concept to wrap one’s head around, it’s important to remember that the forms and shapes that create images are always fundamentally similar.
The alterations are called adversarial perturbations. They’re carefully calculated to move the image’s representation in the AI’s feature space from the region associated with cats to that associated with dogs.
How the attack affects AI models
When a generative AI model is trained on these poisoned samples, it starts associating the features of the unrelated concept (cats) with the target concept (dogs).
Consequently, when prompted to generate images of dogs, the AI model might produce images of cats instead. This is because the model’s understanding of what constitutes a “dog” has been skewed by the poisoned data.
While this doesn’t completely ‘break’ an AI model, it makes it less effective and more unpredictable, which could certainly dent usability.
AI companies will likely fight back against Nightshade and similar techniques, but that’s going to require time and effort.
Impact
A key impact of Nightshade attack is its ‘bleed-through’ effect. This means that the poisoning of one concept can affect related concepts.
For instance, poisoning the concept of ‘dogs’ might also affect how the model generates images of related animals like ‘wolves’ or ‘foxes.’

are corrupted by the poisoning (named the bleed-through effect). Source: University of Chicago via ArXiv
Furthermore, when multiple concepts are poisoned in a model, it can break the model’s ability to generate coherent images for a wide range of prompts.
How artists can use Nightshade
Nightshade is a tool you download and use yourself, but it’s pretty resource-intensive, requiring a compatible Nvidia GPU with at least 4G of memory.
This process could be simplified in the future, or there might be cloud services where you can simply upload your images to be Nightshade’d for you.
Here’s how to use Nightshade:
- Select your artwork: You can either drag a single image into the image placeholder or select multiple images using the “Select…” button.
- Adjust parameters: Intensity determines the strength of Nightshade’s effect. A higher intensity leads to a more potent disruption but may cause noticeable changes to your artwork. Render quality indicates the computation time for finding the optimal poison level. Higher quality equals stronger poison but requires more time. If you have a GPU, this process will be faster.
- Choose output directory: Select where you want the Nightshaded images to be saved.
- Select poison tag: Nightshade operates by misguiding AI about certain concepts in your image. For example, it can alter images tagged as “car” to be perceived as “cow” by AI models. Nightshade will suggest a tag based on its content analysis when selecting your image. Ensure the tag accurately reflects the key concept in your image, and adjust if necessary. The effectiveness of Nightshade increases when your image is associated with this tag through alt-text, captions, or nearby text.
- Run Nightshade: After finalizing your settings and confirming the image tag, start the process by hitting the “Run” button. The altered images will be saved in your chosen output directory.
- Find detailed instructions in the official user guide here.
Community reception to Nightshade reception
There’s been overwhelming support for artists trying to defend their work from AI, but as ever, there are multiple factions, with some likening it to a cyberattack on AI models.
In response to critics, the team clarifies, “Nightshade’s goal is not to break models, but to increase the cost of training on unlicensed data, such that licensing images from their creators becomes a viable alternative.”
“Used responsibly, Nightshade can help deter model trainers who disregard copyrights, opt-out lists, and do-not-scrape/robots.txt directives,” they assert.
The debate surrounding data scraping and AI model training has become extremely bitter following the controversy at Midjourney and a deluge of companies using AI-generated artwork, replacing human labor in the process.
Nightshade is out!
Nightshade poisons AI models if your art or images are taken without permission, Glaze protects you from AI mimicry. It’s recommended you Nightshade first, then Glaze. A version that does both is coming.
Read this thread for more info.
Go get ’em 🫡 https://t.co/bU8EDthUcS pic.twitter.com/YddNu8xmJm
— Reid Southen (@Rahll) January 19, 2024
Suddenly, it feels like there’s a widening void between tech companies marketing AI as a philanthropic force and the public, who feel that it’s encroaching too far into culture and society.
Indeed, Nightshade isn’t just useful for artists. People are encouraging as many to use these tools as possible, creating a smaller pool of high-quality data for AI companies to scrape.
Do companies have enough data already, though? Maybe for now, but to keep models contemporary and updated, AI developers will need to induct new data into their systems at some point.
#nightshade
Pro tip: use Nightshade on everything you upload online (not only your art), social media pictures, daily photos about your meal, family, puppies, kittens, random selfies and street shots – and let the game begin.— edit ballai 🌿 (@eballai) January 19, 2024
In Glaze and Nightshade, we’re seeing an emerging technological and ethical battle between creators and AI companies.
It’s going to get more and more interesting, and might there be similar ways of deceiving and poisoning language models?
This, combined with legal battles, could see generative AI enter a volatile period. It’s going to be a huge year for the technology.





